An important aspect of bioplastics is their biodegradability. Thus, they can be completely degradable or not degrade at all. Biodegradable plastics are materials that can be broken down by microorganisms in nature. This means that over time, these materials decompose into natural components such as carbon, water and biomass. The microorganisms can be thought of as super small animals that feed on the bioplastic and thus metabolize it. Of course, this only works if the bioplastic is completely biodegradable, otherwise our little animals won't go for it. Over time, the plastic then breaks into smaller and smaller pieces, leaving behind microplastics that cannot be decomposed.
On another level, the origin of the plastic must also be considered. We are most familiar with the petrochemical or petroleum-based plastics, as we encounter these everywhere in everyday life. On the opposite side, there are the bio-based plastics, which are made entirely from sustainable and renewable raw materials.
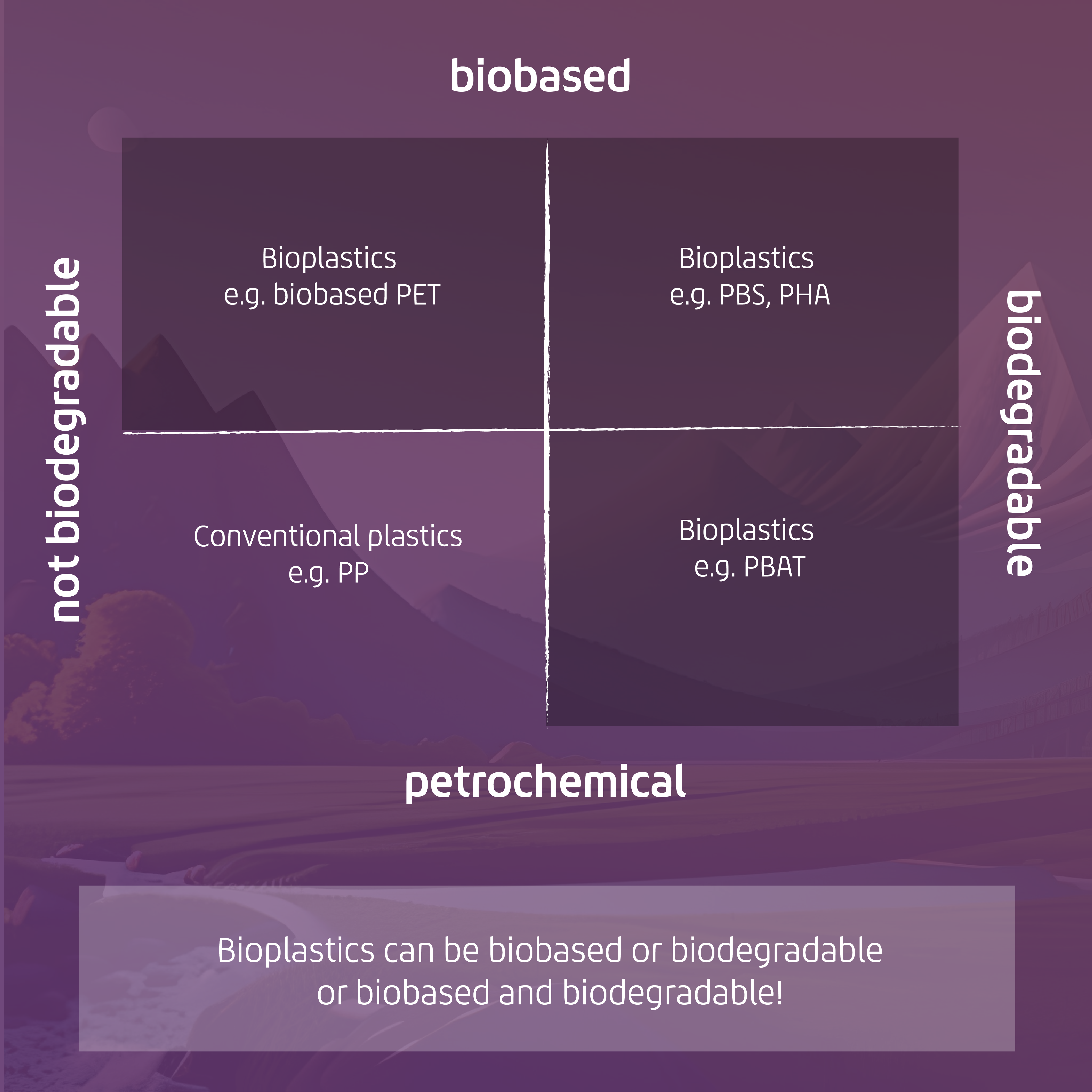
In combination, one can then form a matrix in which the various (bio)plastics can be used. At the bottom left are the conventional plastics, which are petroleum-based and not biodegradable. To the right are the petroleum-based bioplastics that are biodegradable, such as PBAT. In contrast, there are bioplastics of natural origin, biobased, which are not biodegradable. In the upper right corner are the fully biobased and biodegradable plastics. Depending on the application, the latter should always be used as an alternative, as this way we promote the conservation of resources and at the same time do not leave behind microplastics.
The introduction of bioplastics is therefore an important step in the right direction and can help reduce the impact of plastics on the environment. Together we can create a more sustainable future! 🌱💚
#bioplastics #biodegradability #sustainability #environmental protection




